|
PaGMO
1.1.5
|
|
PaGMO
1.1.5
|
The Firefly algorithm. More...
#include <firefly.h>
Public Member Functions | |
| firefly (int gen=1, double alpha=0.01, double beta=1.0, double gamma=0.8) | |
| Constructor. More... | |
| base_ptr | clone () const |
| Clone method. | |
| void | evolve (population &) const |
| Evolve implementation. More... | |
| std::string | get_name () const |
| Algorithm name. | |
 Public Member Functions inherited from pagmo::algorithm::base Public Member Functions inherited from pagmo::algorithm::base | |
| base () | |
| Default constructor. More... | |
| virtual | ~base () |
| Trivial destructor. More... | |
| std::string | human_readable () const |
| Return human readable representation of the algorithm. More... | |
| void | set_screen_output (const bool p) |
| Setter-Getter for protected m_screen_output data. More... | |
| bool | get_screen_output () const |
| Gets screen output. More... | |
| void | reset_rngs (const unsigned int) const |
| Resets the seed of the internal rngs using a user-provided seed. More... | |
Protected Member Functions | |
| std::string | human_readable_extra () const |
| Extra human readable algorithm info. More... | |
Friends | |
| class | boost::serialization::access |
Additional Inherited Members | |
 Protected Attributes inherited from pagmo::algorithm::base Protected Attributes inherited from pagmo::algorithm::base | |
| bool | m_screen_output |
| Indicates to the derived class whether to print stuff on screen. | |
| rng_double | m_drng |
| Random number generator for double-precision floating point values. | |
| rng_uint32 | m_urng |
| Random number generator for unsigned integer values. | |
| unsigned int | m_fevals |
| A counter for the number of function evaluations. | |
The Firefly algorithm.
The firefly algorithm (FA) is a metaheuristic algorithm, inspired by the flashing behaviour of fireflies.
At each call of the evolve method a number of function evaluations equal to gen * pop.size() * pop.size() is performed.
NOTE: when called on mixed-integer problems Firefly treats the integer part as fixed and optimizes the continuous part.
The algorithm used is the one provided in the first paper attached with 2 differences:
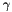 is calculated with the adaptive method explained in the second paper attached (Equation 3) The attactiveness is calculated as
is calculated with the adaptive method explained in the second paper attached (Equation 3) The attactiveness is calculated as 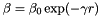
These modifications make the algorithm perform better on all the test problems we experimented.
| pagmo::algorithm::firefly::firefly | ( | int | gen = 1, |
| double | alpha = 0.01, |
||
| double | beta = 1.0, |
||
| double | gamma = 0.8 |
||
| ) |
Constructor.
Allows to specify in detail all the parameters of the algorithm.
| [in] | gen | number of iterations. |
| [in] | alpha | define the width of the random vector |
| [in] | beta | define the maximum attractiveness |
| [in] | gamma | define the absorption coefficent |
| value_error | if number of iterations is negative or alpha, beta and gamma are not in [0,1] |
Definition at line 51 of file firefly.cpp.
|
virtual |
Evolve implementation.
Run the Firefly algorithm for the number of generations specified in the constructors.
| [in,out] | pop | input/output pagmo::population to be evolved. |
Implements pagmo::algorithm::base.
Definition at line 78 of file firefly.cpp.
|
protectedvirtual |
Extra human readable algorithm info.
Will return a formatted string displaying the parameters of the algorithm.
Reimplemented from pagmo::algorithm::base.
Definition at line 212 of file firefly.cpp.
 1.8.9.1
1.8.9.1