Covariance Matrix Adaptation Evolutionary Strategy (CMA-ES)#
#include <pagmo/algorithms/cmaes.hpp>
-
class cmaes#
Covariance Matrix Adaptation Evolutionary Strategy.
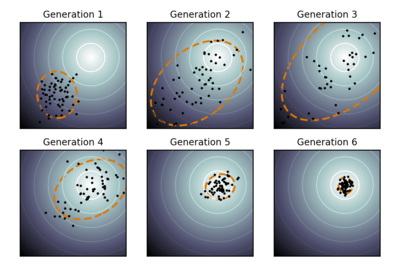
CMA-ES is one of the most successful algorithm, classified as an Evolutionary Strategy, for derivative-free global optimization. The version implemented in PaGMO is the “classic” version described in the 2006 paper titled “The CMA evolution strategy: a comparing review.”.
See also
Hansen, Nikolaus. “The CMA evolution strategy: a comparing review.” Towards a new evolutionary computation. Springer Berlin Heidelberg, 2006. 75-102.
Note
This user-defined algorithm is available only if pagmo was compiled with the
PAGMO_WITH_EIGEN3option enabled (see the installation instructions).Note
Since at each generation all newly generated individuals sampled from the adapted distribution are reinserted into the population, CMA-ES may not preserve the best individual (not elitist). As a consequence the plot of the population best fitness may not be perfectly monotonically decreasing.
Warning
A moved-from pagmo::cmaes is destructible and assignable. Any other operation will result in undefined behaviour.
Public Types
-
typedef std::tuple<unsigned, unsigned long long, double, double, double, double> log_line_type#
Single data line for the algorithm’s log.
A log data line is a tuple consisting of:
the generation number,
the number of function evaluations
the best fitness vector so far,
the population flatness evaluated as the distance between the decisions vector of the best and of the worst individual,
the population flatness evaluated as the distance between the fitness of the best and of the worst individual.
-
typedef std::vector<log_line_type> log_type#
Log type.
The algorithm log is a collection of cmaes::log_line_type data lines, stored in chronological order during the optimisation if the verbosity of the algorithm is set to a nonzero value (see cmaes::set_verbosity()).
Public Functions
-
cmaes(unsigned gen = 1, double cc = -1, double cs = -1, double c1 = -1, double cmu = -1, double sigma0 = 0.5, double ftol = 1e-6, double xtol = 1e-6, bool memory = false, bool force_bounds = false, unsigned seed = pagmo::random_device::next())#
Constructor.
Constructs cmaes
- Parameters
gen – number of generations.
cc – backward time horizon for the evolution path (by default is automatically assigned)
cs – makes partly up for the small variance loss in case the indicator is zero (by default is automatically assigned)
c1 – learning rate for the rank-one update of the covariance matrix (by default is automatically assigned)
cmu – learning rate for the rank- \(\mu\) update of the covariance matrix (by default is automatically assigned)
sigma0 – initial step-size
ftol – stopping criteria on the x tolerance (default is 1e-6)
xtol – stopping criteria on the f tolerance (default is 1e-6)
memory – when true the adapted parameters are not reset between successive calls to the evolve method
force_bounds – when true the box bounds are enforced. The fitness will never be called outside the bounds but the covariance matrix adaptation mechanism will worsen
seed – seed used by the internal random number generator (default is random)
- Throws
std::invalid_argument – if cc, cs, c1 and cmu are not in [0, 1]
-
population evolve(population) const#
Algorithm evolve method.
Evolves the population for a maximum number of generations, until one of tolerances set on the population flatness (x_tol, f_tol) are met.
- Parameters
pop – population to be evolved
- Throws
std::invalid_argument – if the problem is multi-objective or constrained
std::invalid_argument – if the problem is unbounded
std::invalid_argument – if the population size is not at least 5
- Returns
evolved population
-
void set_seed(unsigned)#
Sets the seed.
- Parameters
seed – the seed controlling the algorithm stochastic behaviour
-
inline unsigned get_seed() const#
Gets the seed.
- Returns
the seed controlling the algorithm stochastic behaviour
-
inline void set_verbosity(unsigned level)#
Sets the algorithm verbosity.
Sets the verbosity level of the screen output and of the log returned by get_log().
levelcan be:0: no verbosity
>0: will print and log one line each
levelgenerations.
Example (verbosity 1):
Gen, is the generation number, Fevals the number of function evaluation used, Best is the best fitness function currently in the population, dx is the norm of the distance to the population mean of the mutant vectors, df is the population flatness evaluated as the distance between the fitness of the best and of the worst individual and sigma is the current step-sizeGen: Fevals: Best: dx: df: sigma: 51 1000 1.15409e-06 0.00205151 3.38618e-05 0.138801 52 1020 3.6735e-07 0.00423372 2.91669e-05 0.13002 53 1040 3.7195e-07 0.000655583 1.04182e-05 0.107739 54 1060 6.26405e-08 0.00181163 3.86002e-06 0.0907474 55 1080 4.09783e-09 0.000714699 3.57819e-06 0.0802022 56 1100 1.77896e-08 4.91136e-05 9.14752e-07 0.075623 57 1120 7.63914e-09 0.000355162 1.10134e-06 0.0750457 58 1140 1.35199e-09 0.000356034 2.65614e-07 0.0622128 59 1160 8.24796e-09 0.000695454 1.14508e-07 0.04993
- Parameters
level – verbosity level
-
inline unsigned get_verbosity() const#
Gets the verbosity level.
- Returns
the verbosity level
-
inline unsigned get_gen() const#
Gets the generations.
- Returns
the number of generations to evolve for
-
void set_bfe(const bfe &b)#
Sets the bfe.
Sets the batch function evaluation scheme.
- Parameters
b – batch function evaluation object
-
inline std::string get_name() const#
Algorithm name.
One of the optional methods of any user-defined algorithm (UDA).
- Returns
a string containing the algorithm name
-
std::string get_extra_info() const#
Extra info.
One of the optional methods of any user-defined algorithm (UDA).
- Returns
a string containing extra info on the algorithm
-
inline const log_type &get_log() const#
Get log.
A log containing relevant quantities monitoring the last call to evolve. Each element of the returned
std::vectoris a cmaes::log_line_type containing: Gen, Fevals, Best, dx, df, sigma as described in cmaes::set_verbosity- Returns
an
std::vectorof cmaes::log_line_type containing the logged values Gen, Fevals, Best, dx, df, sigma
-
typedef std::tuple<unsigned, unsigned long long, double, double, double, double> log_line_type#