Non dominated sorting genetic algorithm (NSGA-II)#
-
class nsga2#
Nondominated Sorting genetic algorithm II (NSGA-II)
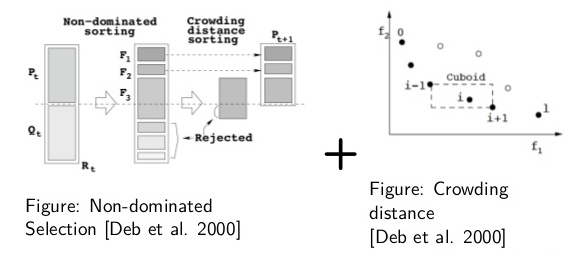
NSGA-II is a solid multi-objective algorithm, widely used in many real-world applications. While today it can be considered as an outdated approach, nsga2 has still a great value, if not as a solid benchmark to test against. NSGA-II generates offsprings using a specific type of crossover and mutation and then selects the next generation according to nondominated-sorting and crowding distance comparison.
The version implemented in pagmo can be applied to box-bounded multiple-objective optimization. It also deals with integer chromosomes treating the last
int_dimentries in the decision vector as integers.See: Deb, K., Pratap, A., Agarwal, S., & Meyarivan, T. A. M. T. (2002). A fast and elitist multiobjective genetic algorithm: NSGA-II. IEEE transactions on evolutionary computation, 6(2), 182-197.
Public Types
-
typedef std::tuple<unsigned, unsigned long long, vector_double> log_line_type#
Single entry of the log (gen, fevals, ideal_point)
-
typedef std::vector<log_line_type> log_type#
The log.
Public Functions
-
nsga2(unsigned gen = 1u, double cr = 0.95, double eta_c = 10., double m = 0.01, double eta_m = 50., unsigned seed = pagmo::random_device::next())#
Constructor.
Constructs the NSGA II user defined algorithm.
- Parameters
gen – [in] Number of generations to evolve.
cr – [in] Crossover probability.
eta_c – [in] Distribution index for crossover.
m – [in] Mutation probability.
eta_m – [in] Distribution index for mutation.
seed – seed used by the internal random number generator (default is random)
- Throws
std::invalid_argument – if
cris not \( \in [0,1[\),mis not \( \in [0,1]\),eta_cis not in [1,100[ oreta_mis not in [1,100[.
-
population evolve(population) const#
Algorithm evolve method.
Evolves the population for the requested number of generations.
- Parameters
pop – population to be evolved
- Throws
std::invalid_argument – if pop.get_problem() is stochastic, single objective or has non linear constraints. If
int_dimis larger than the problem dimension. If the population size is smaller than 5 or not a multiple of 4.- Returns
evolved population
-
void set_seed(unsigned)#
Sets the seed.
- Parameters
seed – the seed controlling the algorithm stochastic behaviour
-
inline unsigned get_seed() const#
Gets the seed.
- Returns
the seed controlling the algorithm stochastic behaviour
-
inline void set_verbosity(unsigned level)#
Sets the algorithm verbosity.
Sets the verbosity level of the screen output and of the log returned by get_log().
levelcan be:0: no verbosity
>0: will print and log one line each
levelgenerations.
Example (verbosity 1):
Gen, is the generation number, Fevals the number of function evaluation used. The ideal point of the current population follows cropped to its 5th component.Gen: Fevals: ideal1: ideal2: ideal3: 1 0 0.0257554 0.267768 0.974592 2 52 0.0257554 0.267768 0.908174 3 104 0.0257554 0.124483 0.822804 4 156 0.0130094 0.121889 0.650099 5 208 0.00182705 0.0987425 0.650099 6 260 0.0018169 0.0873995 0.509662 7 312 0.00154273 0.0873995 0.492973 8 364 0.00154273 0.0873995 0.471251 9 416 0.000379582 0.0873995 0.471251 10 468 0.000336743 0.0855247 0.432144
- Parameters
level – verbosity level
-
inline unsigned get_verbosity() const#
Gets the verbosity level.
- Returns
the verbosity level
-
void set_bfe(const bfe &b)#
Sets the batch function evaluation scheme.
- Parameters
b – batch function evaluation object
-
inline std::string get_name() const#
Algorithm name.
Returns the name of the algorithm.
- Returns
std::stringcontaining the algorithm name
-
std::string get_extra_info() const#
Extra info.
Returns extra information on the algorithm.
- Returns
an
std::stringcontaining extra info on the algorithm
-
inline const log_type &get_log() const#
Get log.
A log containing relevant quantities monitoring the last call to evolve. Each element of the returned
std::vectoris a nsga2::log_line_type containing: Gen, Fevals, ideal_point as described in nsga2::set_verbosity- Returns
an
std::vectorof nsga2::log_line_type containing the logged values Gen, Fevals, ideal_point
-
typedef std::tuple<unsigned, unsigned long long, vector_double> log_line_type#