Monotonic Basin Hopping (MBH) - Generalized#
-
class mbh#
Monotonic Basin Hopping (generalized).
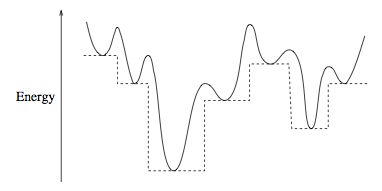
Monotonic basin hopping, or simply, basin hopping, is an algorithm rooted in the idea of mapping the objective function \(f(\mathbf x_0)\) into the local minima found starting from \(\mathbf x_0\). This simple idea allows a substantial increase of efficiency in solving problems, such as the Lennard-Jones cluster or the MGA-1DSM interplanetary trajectory problem that are conjectured to have a so-called funnel structure.
In pagmo we provide an original generalization of this concept resulting in a meta-algorithm that operates on any pagmo::population using any suitable user-defined algorithm (UDA). When a population containing a single individual is used and coupled with a local optimizer, the original method is recovered. The pseudo code of our generalized version is:
> Create a pagmo::population > Select a UDA > Store best individual > while i < stop_criteria > > Perturb the population in a selected neighbourhood > > Evolve the population using the algorithm > > if the best individual is improved > > > increment i > > > update best individual > > else > > > i = 0
pagmo::mbh is a user-defined algorithm (UDA) that can be used to construct pagmo::algorithm objects.
See: https://arxiv.org/pdf/cond-mat/9803344.pdf for the paper introducing the basin hopping idea for a Lennard-Jones cluster optimization.
Public Types
-
typedef std::tuple<unsigned long long, double, vector_double::size_type, double, unsigned> log_line_type#
Single entry of the log (feval, best fitness, n. constraints violated, violation norm, trial).
-
typedef std::vector<log_line_type> log_type#
The log.
Public Functions
-
mbh()#
Default constructor.
The default constructor will initialize the algorithm with the following parameters:
inner algorithm: pagmo::compass_search;
consecutive runs of the inner algorithm that need to result in no improvement for pagmo::mbh to stop: 5;
scalar perturbation: 1E-2;
seed: random.
- Throws
unspecified – any exception thrown by the constructor of pagmo::algorithm.
-
template<typename T, ctor_enabler<T> = 0>
inline explicit mbh(T &&a, unsigned stop, double perturb, unsigned seed = pagmo::random_device::next())# Constructor (scalar perturbation).
This constructor will construct a monotonic basin hopping algorithm using a scalar perturbation.
Note
This constructor is enabled only if
Tcan be used to construct apagmo::algorithm.- Parameters
a – a user-defined algorithm (UDA) or a pagmo::algorithm that will be used to construct the inner algorithm.
stop – consecutive runs of the inner algorithm that need to result in no improvement for pagmo::mbh to stop.
perturb – the perturbation to be applied to each component of the decision vector of the best population found when generating a new starting point. These are defined relative to the corresponding bounds.
seed – seed used by the internal random number generator (default is random).
- Throws
unspecified – any exception thrown by the constructor of pagmo::algorithm.
std::invalid_argument – if
perturbis not in the (0,1] range.
-
template<typename T, ctor_enabler<T> = 0>
inline explicit mbh(T &&a, unsigned stop, vector_double perturb, unsigned seed = pagmo::random_device::next())# Constructor (vector perturbation).
This constructor will construct a monotonic basin hopping algorithm using a vector perturbation.
Warning
This constructor is enabled only if
T, after the removal of cv/reference qualifiers, is notpagmo::algorithm.- Parameters
a – a user-defined algorithm (UDA) or a pagmo::algorithm that will be used to construct the inner algorithm.
stop – consecutive runs of the inner algorithm that need to result in no improvement for pagmo::mbh to stop.
perturb – a pagmo::vector_double with the perturbations to be applied to each component of the decision vector of the best population found when generating a new starting point. These are defined relative to the corresponding bounds.
seed – seed used by the internal random number generator (default is random).
- Throws
unspecified – any exception thrown by the constructor of pagmo::algorithm.
std::invalid_argument – if not all the elements of
perturbare in the (0,1] range.
-
population evolve(population) const#
Evolve method.
This method will evolve the input population up to when
stopconsecutive runs of the internal algorithm do not improve the solution.- Parameters
pop – population to be evolved.
- Throws
std::invalid_argument – if the problem is multi-objective or stochastic, or if the perturbation vector size does not equal the problem size.
- Returns
evolved population.
-
void set_seed(unsigned)#
Set the seed.
- Parameters
seed – the seed controlling the algorithm’s stochastic behaviour.
-
inline unsigned get_seed() const#
Get the seed.
- Returns
the seed controlling the algorithm’s stochastic behaviour.
-
inline void set_verbosity(unsigned level)#
Set the algorithm verbosity.
This method will sets the verbosity level of the screen output and of the log returned by get_log().
levelcan be:0: no verbosity,
>0: will print and log one line at the end of each call to the inner algorithm.
Example (verbosity 100):
Fevals: Best: Violated: Viol. Norm: Trial: 105 110.395 1 0.0259512 0 i 211 110.395 1 0.0259512 1 i 319 110.395 1 0.0259512 2 i 422 110.514 1 0.0181383 0 i 525 111.33 1 0.0149418 0 i 628 111.33 1 0.0149418 1 i 731 111.33 1 0.0149418 2 i 834 111.33 1 0.0149418 3 i 937 111.33 1 0.0149418 4 i 1045 111.33 1 0.0149418 5 i
Fevalsis the number of fitness evaluations,Bestis the objective function of the best fitness currently in the population,Violatedis the number of constraints currently violated by the best solution,Viol. Normis the norm of the violation (discounted already by the constraints tolerance) andTrialis the trial number (which will determine the algorithm stop). The smalliappearing at the end of the line stands for “infeasible” and will disappear only onceViolatedis 0.- Parameters
level – verbosity level.
-
inline unsigned get_verbosity() const#
Get the verbosity level.
- Returns
the verbosity level.
-
inline const vector_double &get_perturb() const#
Get the perturbation vector.
- Returns
a const reference to the perturbation vector.
-
void set_perturb(const vector_double&)#
Set the perturbation vector.
- Parameters
perturb – the perturbation vector.
- Throws
std::invalid_argument – if not all the components of the perturbation vector are in the (0,1] range.
-
thread_safety get_thread_safety() const#
Algorithm’s thread safety level.
The thread safety of this meta-algorithm is the minimum between the thread safety of the internal pagmo::algorithm and the basic thread safety level. I.e., this algorithm never provides more than the basic thread safety level.
- Returns
the thread safety level of this algorithm.
-
inline const algorithm &get_inner_algorithm() const#
Getter for the inner algorithm.
Returns a const reference to the inner pagmo::algorithm.
- Returns
a const reference to the inner pagmo::algorithm.
-
inline algorithm &get_inner_algorithm()#
Getter for the inner algorithm.
Returns a reference to the inner pagmo::algorithm.
Warning
The ability to extract a non const reference is provided only in order to allow to call non-const methods on the internal
pagmo::algorithminstance. Assigning a newpagmo::algorithmvia this reference is undefined behaviour.- Returns
a reference to the inner pagmo::algorithm.
-
inline const log_type &get_log() const#
Get log.
A log containing relevant quantities monitoring the last call to mbh::evolve(). Each element of the returned
std::vectoris a mbh::log_line_type containing:Fevals,Best,Violated,Viol.NormandTrialas described in mbh::set_verbosity().- Returns
an
std::vectorof mbh::log_line_type containing the logged values Fevals, Best, Violated, Viol.Norm and Trial.
-
inline std::string get_name() const#
Algorithm name.
- Returns
a string containing the algorithm name.
-
std::string get_extra_info() const#
Extra info.
- Returns
a string containing extra info on the algorithm.
-
typedef std::tuple<unsigned long long, double, vector_double::size_type, double, unsigned> log_line_type#